HIV and Injection Drug Use | Syringe Services Programs for HIV Prevention

Harm Reduction
AIDS Research Articles and News
Hepatitis C Research Articles and News
Syringe and Needle Exchange Programs
Drug War
Drug Policy Reform
Overview
Originally Published: 11/30/2016
Post Date: 11/30/2016
by CDC
Summary/Abstract
Center for Disease Control report (CDC) on HIV and Injection Drug Use and how Syringe Services Programs help prevent HIV and Hepatitis C infection.
Content
HIV and Injection Drug Use
Syringe Services Programs for HIV Prevention
Sharing needles, syringes, and other injection equipment puts people who inject drugs (PWID) at high risk for getting HIV and other infections, including hepatitis. Annual HIV diagnoses among black and Hispanic/Latino PWID were cut in half between 2008–2014, but diagnoses among white PWID dropped by only 28%. One reason may be that fewer blacks and Hispanics/Latinos are sharing needles and syringes, while whites are more likely to share them. Syringe services programs (SSPs) can play a role in preventing HIV and other health problems among PWID. They provide access to sterile syringes and should also provide comprehensive services such as help with stopping substance misuse; testing and linkage to treatment for HIV, hepatitis B, and hepatitis C; education on what to do for an overdose; and other prevention services. State and local health departments can work with their lawmakers and law enforcement to make SSPs more available to PWID.
State and local health departments can:
- Use data on HIV, hepatitis, substance use, and overdoses to determine where services are needed.
- Work with law enforcement and local leaders to expand access to SSPs, where permitted by law.
- Provide HIV and hepatitis testing and prevention services for PWID.
- Ensure treatment is available for overdoses, HIV, hepatitis, and substance use disorder, and inform first responders about available resources.
- 1 in 10 HIV diagnoses are among people who inject drugs (PWID).
- More than half of PWID used a syringe services program in 2015.
- Only 1 in 4 PWID got all their syringes from sterile sources in 2015.
Problem
HIV diagnoses among PWID have decreased, but progress has been uneven.
The number of PWID getting HIV has been cut in half in the U.S.
- Annual HIV diagnoses among PWID decreased by 48% overall (2008–2014).
- Annual HIV diagnoses fell by about 50% among black and Hispanic/Latino PWID, both in urban and nonurban areas (2008–2014).
- Annual HIV diagnoses dropped by 28% among urban white PWID during 2008–2012, but did not decrease from 2012–2014. Trends among nonurban whites were similar.
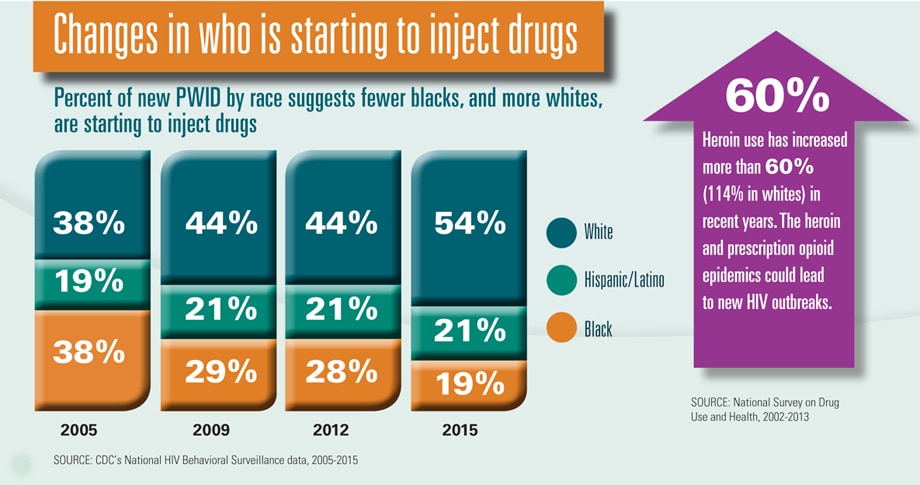
There have been changes in who is starting to inject drugs.*
- In 2005, blacks and whites each made up 38% of new PWID (those who have been injecting for 5 years or less).
- In 2015, blacks made up 19% of new PWID and whites made up 54%.
- The percent of new PWID who are Hispanic/Latino stayed around the same at about 21%.
Some PWID are at higher risk for getting HIV from sharing syringes.*
- About 46% of new white PWID shared syringes, compared with 32% of Hispanics/Latinos and 28% of blacks.
- White PWID started injecting at younger ages than other races/ethnicities, and younger people were more likely to share syringes.
- Syringe sharing was low (13%) among PWID who got all their syringes from sterile sources like SSPs, but high (41%) among those who didn’t.
*In 22 cities with a high number of HIV cases
What Can Be Done
The Federal government is
-
Allowing certain state and local prevention programs to use their federal funds for SSPs (not to buy needles, syringes, and other injection equipment). For more information, visit http://bit.ly/2eVU8ab.
-
Providing support and access to HIV, hepatitis, and substance use disorder prevention and treatment, including medication-assisted treatment and mental health services.
- Providing guidelines to healthcare providers for appropriate prescribing practices to reduce opioid abuse and overdoses.
- Monitoring national trends for HIV, hepatitis, and drug overdoses.
State and local health departments can
- Use data on HIV, hepatitis, substance use, and overdoses to determine where services are needed.
- Work with law enforcement and local leaders to expand access to SSPs, where permitted by law.
- Provide HIV and hepatitis testing and prevention services for PWID.
- Ensure treatment is available for overdoses, HIV, hepatitis, and substance use disorder, and inform first responders about available resources.
Healthcare providers can
- Screen patients for substance use disorder, including the misuse of prescription opioids. Provide or link PWID to medication-assisted treatment, and link them to mental health services, if needed. Use CDC opioid prescribing guidelines, http://bit.ly/1jTLLej
- Test PWID for HIV and hepatitis and treat them if they are infected. Vaccinate patients for hepatitis A and B, if appropriate.
- Prescribe sterile syringes to PWID, or refer them to SSPs or pharmacies that provide sterile syringes, where permitted by law.
- Provide or refer PWID to HIV risk reduction counseling. Consider prescribing pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) for PWID at very high HIV risk.
- Prevent overdose deaths by providing naloxone or referring PWID to pharmacies or community-based programs that provide it, where permitted by law.
Lawmakers, judges, police and other criminal justice officials can
-
Address legal and law enforcement barriers that prevent or discourage the use of SSPs and substance use disorder treatment, including use of medication-assisted treatment.
-
Refer PWID to substance use disorder treatment and HIV and hepatitis prevention services.
-
Support HIV and hepatitis testing and care and hepatitis vaccination in prisons and jails.